What is Ideal speed of a Bowling Ball & Calculate It
Bowling is an adaptive sport because the speed of your bowling ball must account for and conform to factors such as type of coverstock, power, hook, and lane conditions. Controlling the speed of a bowling ball is an essential skill every pro bowler has to master at one point. Here is the ultimate guide for controlling the speed of your bowling ball.
The speed of your bowling ball is a critical element that you must master if you are to get the best scores. Controlling the seed of your bowling bowl is important because too little of it and the ball won’t reach the pins, and too much of it can interfere with your aim. You must be wondering about the ideal speed and how to control the speed of a bowling ball. You can read the article below to understand how the speed of a bowling ball affects your game.
How does the Speed of a Bowling Ball Affect Your Game?
The speed of your bowling ball affects the power of impact when the ball hits the pins. Fast bowling speeds are essential for powerful collisions when the ball hits the pins. The pace of your bowling ball also affects the hook on your ball. Tweaking the tempo on a bowling ball helps control the curving effect on a bowling ball as it rolls towards the pins.
What are the Factors that can affect the Speed of your Bowling Ball?
Bowlers determine the speed of their bowling ball when approaching the foul line. However, other factors can affect the speed of the bowling ball after you release the ball. The factors that can affect the speed of your bowling ball include the following.
1. Coverstock Material

The type of coverstock material affects the speed of your bowling ball because different materials have different frictional coefficient values. A solid coverstock bowling ball with a low-grit surface texture will travel slower than a polished pearl reactive coverstock with a low-grit surface texture when rolling down the same bowling lane. The speed of the two bowling balls will vary even when thrown by a single bowler down the same bowling lane.
2. Lane Status

The condition of a bowling lane is an essential factor when determining the speed of a bowling ball. A dry bowling lane, for example, will slow down the speed of a bowling ball more than an oily lane. The amount of oil on a bowling lane determines the frictional coefficient between the lane surface and the ball, thus affecting the speed of the bowling ball.
3. Bowling Hook

The hook on your bowling ball also determines the speed when rolling down the bowling lane. The greater the revolution rate on a bowling hook, the greater the speed loss on a bowling ball as it gets closer to the pins. The revolution rate on a bowling ball also varies depending on the size (ten-pin, five-pin, or candle-pin) of the bowling ball.
Methods for Finding the Speed of a Bowling Ball?
You can use two methods to find the speed of your bowling ball, and they include using:
A. Computer-Aided Tracking Systems
The first method is using a Computer Aided Tracking System (C.A.T.S.) to know the exact speed of your bowling ball. However, Computer Aided Tracking Systems are present in pro bowling competitions/tournaments like on PBA televised shows. The accuracy of speed measurement depends on the level of the bowling tournament. Speed measurement using C.A.T.S. is more accurate in high-level bowling tournaments because speed monitoring happens throughout the bowling lane.
B. Stopwatch

The second method for knowing the speed of your bowling ball is using a stopwatch and a bowling speed chart. You can use this method in local bowling leagues or when practicing. You can follow the steps below to calculate the speed of your bowling ball using a stopwatch and chart.
1. Find an accurate digital stopwatch and have someone start recording the time after you release the bowling ball until the pin impact moment.
2. Bowl a series of at least five throws in a row before averaging the time in seconds.
3. Find the speed of your bowling ball by comparing the average ball speed to the time on the speed chart below.
- Speed – 3.0 seconds = 13.9 mph
- Speed – 2.9 seconds = 14.4 mph
- Speed – 2.8 seconds = 14.9 mph
- Speed – 2.7 seconds = 15.4 mph
- Speed – 2.6 seconds = 16.0 mph
- Speed – 2.5 seconds = 16.7 mph
- Speed – 2.4 seconds = 17.4 mph
- Speed – 2.3 seconds = 18.1 mph
- Speed – 2.2 seconds = 19.0 mph
- Speed – 2.1 seconds = 19.9 mph
- Speed – 2.0 seconds = 20.8 mph
However, the chart only shows speed estimates, and you should account for a (+/-0.15 seconds) margin of error while calculating the speed of your bowling ball.
What is the Recommended Bowling Ball Speed?
The ideal bowling ball speed is subjective and depends on the above factors and bowling techniques. However, according to a study report from the United States Bowling Congress (USBC), the ideal bowling ball speed stands at 16 mph -17 mph upon pin impact. Pro bowlers have a ball speed of around 20 mph – 22 mph upon pin impact. Your bowling speed upon release should be around 20 mph – 22 mph, accounting for speed loss to achieve the 16 mph -17 mph upon pin impact.
How to Increase/Decrease Bowling Ball Speed?
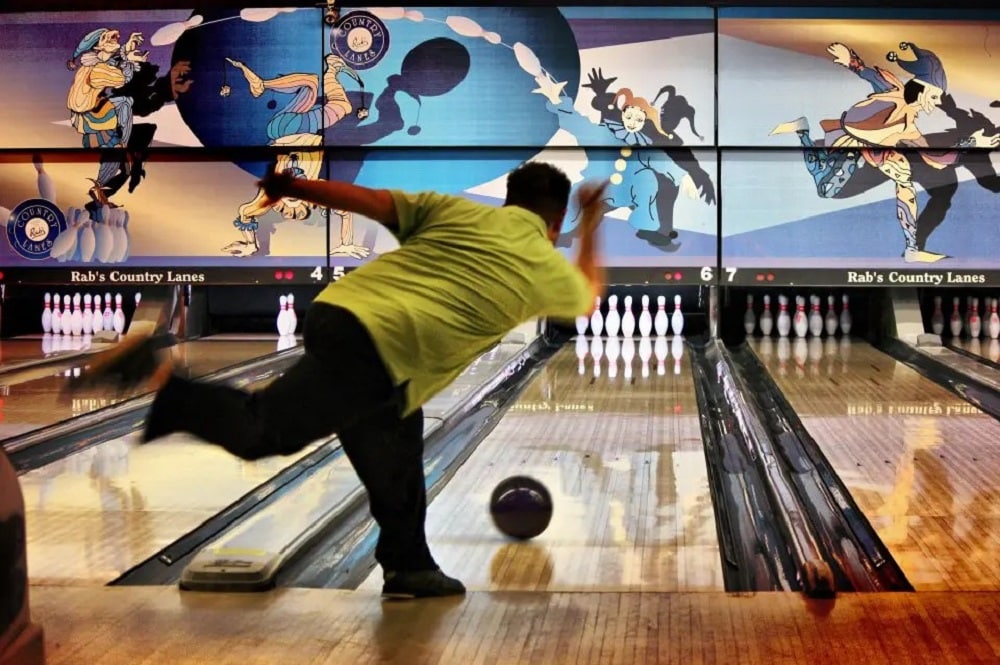

The method for increasing/decreasing bowling ball speed depends on the elevation of the ball before the approach and steps while approaching the lane. A high ball elevation before the lane approach increases the speed of the ball because of gravitational pull after releasing the ball, whereas a lower ball elevation decreases the acceleration of the bowling ball. A longer stride during the approach increases your ball's speed, whereas shorter strides decrease the ball's acceleration.
Does the faster bowling ball hit more bottle pins?
The speed of the bowling ball can have an impact on how many pins are knocked down, but it's not necessarily true that a faster ball will always hit more pins, including the bottle pins.
When a ball hits the pins, it transfers its energy to them, causing them to move and potentially knock down other pins. A faster ball generally has more energy than a slower ball, which means it can transfer more energy to the pins upon impact. However, if the ball is too fast, it may not have enough time to transfer all of its energy to the pins, resulting in less effective pin action.
In addition to speed, other factors like the ball's angle of entry and rotation can also affect how many pins are knocked down. A ball that enters the pins at the right angle and with the right amount of rotation can create a chain reaction that results in more pins being knocked down.
Conclusion
Bowlers use different bowling bowls and frequent different bowling joints. Doing so can affect the consistency of your performance until you understand how you can use speed variation techniques to take advantage of any bowling lane. You must also practice your bowling skills often to attain consistency in your bowling scores.





![How to Build a Bowling Lane in Your Basement [Installation, and Maintaining]](https://www.bowlingknowledge.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Build-A-Bowling-Lane-In-Your-Basement-At-Home-768x512.jpg)