Are Bowling Balls Hollow or Solid? What are They Made of?
Discover the truth behind the structure of bowling balls and learn what lies beneath their exterior. Find out if they are hollow or solid and what materials make up a modern bowling ball. From inner core to coverstock, this post will discuss all the details of what makes a bowling ball. With that being said, let’s dive in and find answers to the question of whether or not bowling balls are hollow.
Bowling is a worldwide pastime that is appreciated by many individuals. But have you ever wondered what a bowling ball contains? What else do they contain except their smooth exterior? There is considerably more to a bowling ball than first meets the eye. This article addresses the age-old debate of whether bowling balls are solid or hollow. From the inner core to the coverstock, we will present a detailed overview of the components and functions of a bowling ball.
Bowling Ball Components
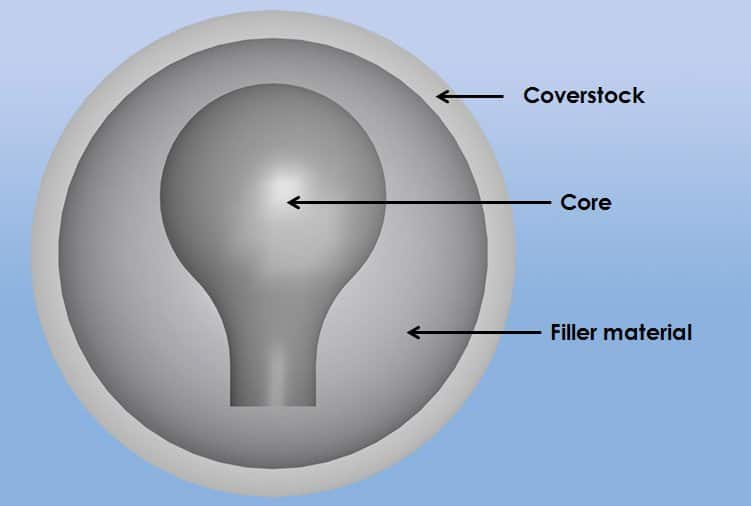
Usually, bowling balls consist of three main parts: the inner core, outer core, and coverstock. However, some types of bowling balls consist of only two parts which include the inner core, and coverstock.
- Coverstock: The outermost layer that affects the ball's color and design, speed, and hooking potential. There are three types of coverstock available: polyester or plastic, urethane, and reactive resin.
- Inner Core: The heaviest part of the ball, made of dense material responsible for most of the ball's weight. In modern balls, the inner core comprises a weight block.
- Outer Core: The lighter material that helps control the ball's speed.
Types of Bowling Ball Cores:
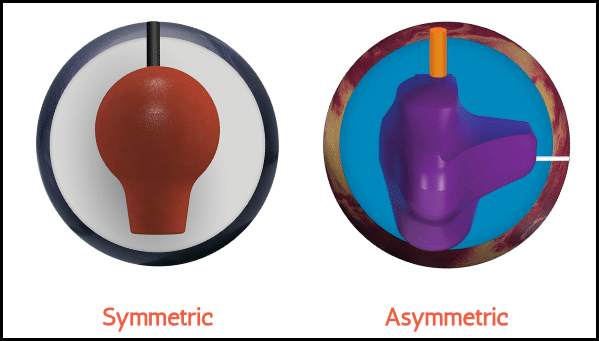
The core or weight block of a bowling ball may come in three main varieties. These include:
- Pancake Cores: No weight block and great for straight bowlers and beginners.
- Symmetrical Cores: Even weight distribution with more hook potential than pancake cores.
- Asymmetrical Cores: Uneven weight distribution with even more hook potential, favored by professional bowlers.
Coverstock Materials:
The coverstock is the outermost cover of a bowling ball. It’s made of the following materials:
- Polyester/Plastic: Strong and durable, good for straight bowlers and beginners.
- Urethane: Soft and flexible with a higher friction coefficient and hook potential.
- Reactive resin: Durable like polyester with hook potential, great for all types of bowlers.
Now that we have learned about the coverstock materials, let’s delve deep and see what’s inside a bowling ball. To begin with, it’s important to note that different filler materials are used to make the core of bowling balls. The density of the filler material determines the overall weight of the ball.
What’s inside a bowling ball?
Inside a bowling ball, there are two main components:
1. Filler material
Most weight blocks are made of glass microbubbles combined with another high-density material. The varied density of the filler material makes for easy adjustment of the weight of bowling balls while maintaining the size.
2. Weight block
The weight block determines how the ball spins and rolls. It is also referred to as the core of the bowling ball. Weight blocks come in different forms including the two-piece ball modified, two-piece ball, three-piece ball varieties, etc. The type of core influences the equilibrium of the ball which ultimately determines how the bowling ball rolls on the plane. Meaning, while some cores allow for snappy or violent hooks, other varieties are designed to produce less aggressive hooks or maybe smoother hooks.
Can liquid be at the Center of a bowling ball?
Contrary to what some people believe, bowling balls do not have a liquid at the center. Instead, they have a solid core, also called the weight block. Among other functions, the solid core aids in regulating the speed of the ball down the lane during any throw. Moreover, a solid core is critical in driving the bowling ball into the pocket, not to mention boosting its hook potential.
Choosing the Right Bowling Ball Type

The material of your bowling ball can greatly influence your performance on the lanes. Here are some tips to help you decide which ball is best for you.
1. For Beginners: Choose Polyester or Plastic Cover
If you're just starting, it's recommended to choose a ball with a polyester or plastic cover. These balls are more affordable and their slippery nature makes them easier to control.
2. Intermediate Bowlers: Go for Urethane Cover
As you progress in your bowling skills, you may want to consider a ball with a urethane cover. Urethane offers good hook potential and better control over your shots, plus it's more durable than other materials.
3. Advanced Bowlers: Reactive Resin Cover is the Way to Go
For those who are looking to elevate their game, a ball with a reactive resin cover is the way to go. Although they are pricier, they offer maximum hook potential, giving you a wider range of possibilities in terms of your strategy.
4. Expert Bowlers: Only Reactive Resin Will Do
For the masters of the sport, a ball with a reactive resin cover is the only choice. You'll need maximum control and longevity, and this material provides just that.
5. Don't Forget about Finger Holes
Regardless of which ball you choose, it's crucial to make sure the finger holes are the correct size and positioned properly for your fingers. If you need more clarification, seek advice from a professional at your local bowling alley or ball shop.
6. Weight Matters Too
The weight of the ball is also a key factor to consider. Heavier balls can be harder to throw, but they have more power upon release. Light balls are easier to throw but lack power. Find the right balance that works for you, starting with a lighter ball if you're a beginner.
7. Pro Bowlers: Pay Attention to the Core
For professional bowlers, the core of the ball is important to consider. It's recommended to try out different cores like pancake, symmetrical, or asymmetrical to see which one works best for you. Your preferred core may not be the one you initially thought was best for you.
The Core's Impact on the Coverstock

Bowling balls are not empty inside; this is where the weight block and filler material play a crucial role in the coverstock or shell. A bowling ball with a solid core wouldn't be able to make the most of these coverstocks, particularly with the intricate aspects such as shells infused with mica.
Polyester or plastic coverstocks have a very smooth surface and are quite hard. This makes them ideal for beginners as they are learning to propel the ball down the lane rather than trying to spin it into the pocket.
Urethane coverstocks are designed for intermediate players. Surprisingly, the smooth surface of the bowling ball is capable of absorbing the oil on the lane, which leads to an increase in friction and a sharper hook. Urethane coverstocks perform better than polyester in this aspect. Reactive resins are considered the ultimate in coverstock technology. They have higher friction-generating capabilities than urethane shells, resulting in sharper hooks. However, they come at a cost as they are not as durable or predictable as the other coverstocks.
Conclusion
Bowling balls are not hollow and consist of three parts: the inner core, outer core, and coverstock. There are different types of cores and coverstocks, each with different characteristics and favored by different types of bowlers. The weight of the ball and the size of the finger holes are also important factors to consider when choosing a ball. Ultimately, the core of the ball plays a crucial role in the coverstock, determining the ball's speed, weight, hooking potential, and other characteristics.

![Can a Bowling Ball Lose Its Hook? [Make It Hook Again]](https://www.bowlingknowledge.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Can-a-Bowling-Ball-Lose-its-Hook-768x512.jpg)



![What Does an F Mean in Bowling? [Don’t be Foul!]](https://www.bowlingknowledge.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/What-Does-an-F-Mean-in-Bowling-768x512.jpg)
![Can I put My Bowling Ball in the Dishwasher? [YES]](https://www.bowlingknowledge.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Can-I-put-My-Bowling-Ball-in-the-Dishwasher-768x512.jpg)